FLEXURAL STRENGTH AND MODULUS
Flexural strength is the measure of the stiffness of a material, that is to say how well it resists bending.

Testing Strength and Modulus
A simple beam of material is supported either end and a load applied at the mid-point. The load is pushed onto the specimen at a constant rate of 2mm per minute.
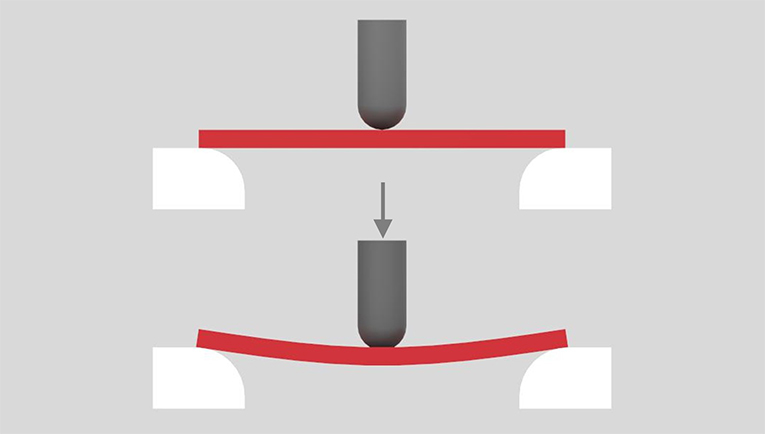
Measurements are taken using at least five values of load and deflection. From these results a deflection curve is plotted from which the flexural modulus is calculated. As with tensile modulus this is a ratio of stress to strain. Values are reported in MPa (psi).
The only difference between ASTM D790 and ISO 178 is the size of the test bar – 125mm x 12.5mm x 3mm and 80mm x 10mm x 4mm respectively. Therefore, the values reported in ASTM and ISO seldom differ significantly.

Typical results for a selection of materials as follows:
| Material | Flex Strength | Flex Modulus |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | 70 | 2.5 |
| Acetal | 85 | 2.5 |
| 30% Glass Filled Acetal | 150 | 7.5 |
| Polypropylene | 40 | 1.5 |
There are various measures which are defined as follows:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Flexural Modulus | The ratio of stress to strain |
| Flexural Stress at Yield | The stress corresponding to test specimen yield |
| Flexural Stress at Break | The stress corresponding to test specimen failure |
| Flexural Strength | The maximum stress sustained by a specimen during testing |